Maps of Suffolk England
Home > Maps of England > Suffolk Maps
Welcome to our Suffolk map page. The map of Suffolk England that is located below is provided by Google Maps. You can "grab" the electronic map and move it around to re-center the map. You can change between standard map view and satellite map view by clicking the small square on the bottom left-hand corner of the map. Satellite map view utilises orbiting satellite and / or aerial high-resolution photography to display images of the map location to street level detail (really quite amazing). Standard map view shows a traditional street map (also known as a road map). You can use the zoom buttons on the bottom right-hand side of the map to zoom in or out to street level detail. We have digital online maps for most towns and cities on the Maps of England page. We also have a good collection of old school printable maps on the Maps of England page.
A map of Suffolk, England
Suffolk Maps
I hope you like the Suffolk County, England street map / road map situated above.
If you like our website, please consider adding a link to the site. These links help to build website traffic and they are considered a vote of confidence for a site.
Suffolk
Suffolk is an East Anglian county of ancient origin in England. It has borders with Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south. The North Sea lies to the east. The county town is Ipswich; other important towns include Lowestoft, Bury St Edmunds, Newmarket, and Felixstowe, one of the largest container ports in Europe.
The county is low-lying but it has quite a few hills (especially more to the west), and has largely arable land with the wetlands of the Broads in the north. The Suffolk Coast and Heaths are an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.
History
Administration
The Anglo-Saxon settlement of Suffolk, and East Anglia generally, occurred on a large scale, possibly following a period of depopulation by the previous inhabitants, the Romanized descendants of the Iceni. By the fifth century, they had established control of the region. The Anglo-Saxon inhabitants later became the "north folk" and the "south folk", from which developed the names "Norfolk" and "Suffolk". Suffolk and several adjacent areas became the kingdom of East Anglia, which later merged with Mercia and then Wessex.
Suffolk was originally divided into four separate Quarter Sessions divisions. In 1860, the number of divisions was reduced to two. The eastern division was administered from Ipswich and the western from Bury St Edmunds. Under the Local Government Act 1888, the two divisions were made the separate administrative counties of East Suffolk and West Suffolk; Ipswich became a county borough. A few Essex parishes were also added to Suffolk: Ballingdon-with-Brundon and parts of Haverhill and Kedington.
On 1 April 1974, under the Local Government Act 1972, East Suffolk, West Suffolk, and Ipswich were merged to form the unified county of Suffolk. The county was divided into several local government districts: Babergh, Forest Heath, Ipswich, Mid Suffolk, St Edmundsbury, Suffolk Coastal, and Waveney. This act also transferred some land near Great Yarmouth to Norfolk. As introduced in Parliament, the Local Government Act would have transferred Newmarket and Haverhill to Cambridgeshire and Colchester from Essex; such changes were not included when the act was passed into law.
In 2007, the Department for Communities and Local Government referred Ipswich Borough Council's bid to become a new unitary authority to the Boundary Committee. The Boundary Committee consulted local bodies and reported in favour of the proposal. It was not, however, approved by the Secretary of State for Communities and Local Government.
Beginning in February 2008, the Boundary Committee again reviewed local government in the county, with two possible options emerging. One was that of splitting Suffolk into two unitary authorities - Ipswich and Felixstowe and Rural Suffolk; and the other, that of creating a single county-wide controlling authority - the "One Suffolk" option. In February 2010, the then-Minister Rosie Winterton announced that no changes would be imposed on the structure of local government in the county as a result of the review, but that the government would be: "asking Suffolk councils and MPs to reach a consensus on what unitary solution they want through a countywide constitutional convention". Following the May 2010 general election, all further moves towards any of the suggested unitary solutions ceased on the instructions of the incoming Coalition government. In 2018 it was determined that Forest Heath and St Edmundsbury would be merged to form a new West Suffolk district, while Waveney and Suffolk Coastal would similarly form a new East Suffolk district. These changes took effect on 1 April 2019.
Archaeology
West Suffolk, like nearby East Cambridgeshire, is renowned for archaeological finds from the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age. Bronze Age artefacts have been found in the area between Mildenhall and West Row, in Eriswell and in Lakenheath. Many bronze objects, such as swords, spearheads, arrows, axes, palstaves, knives, daggers, rapiers, armour, decorative equipment (in particular for horses), and fragments of sheet bronze, are entrusted to St. Edmundsbury heritage service, housed at West Stow just outside Bury St. Edmunds. Other finds include traces of cremations and barrows.
In the east of the county is Sutton Hoo, the site of one of England's most significant Anglo-Saxon archaeological finds, a ship burial containing a collection of treasures including a Sword of State, gold and silver bowls, and jewellery and a lyre.
While carrying out surveys before installing a pipeline in 2014, archaeologists for Anglian Water discovered nine skeletons and four cremation pits, at Bardwell, Barnham, Pakenham and Rougham, all near Bury St Edmunds. Neolithic, Bronze Age, Iron Age, Roman and medieval items were also unearthed, along with the 9 skeletons believed to be of the late or post-Roman era (AD 300-500). Experts said the 5 month project had recovered enough artefacts to fill half a shipping container, and that the discoveries had shed new light on their understanding of the development of small rural communities.
A number of 6th century Anglo-Saxon “grub huts” were also found nearby, which are believed to be cellars beneath Saxon buildings.
In 2019, an excavation of an 4th century Roman cemetery in Great Whelnetham uncovered unusual burial practices. Of 52 skeletons were found, a large number had been decapitated, which archaeologists claimed gave new insight in to Roman traditions. The burial ground includes the remains of men, women and children who likely lived in a nearby settlement. The fact that up to 40% of the bodies were decapitated represents "quite a rare find".
A survey in 2020 named Suffolk the third best place in the UK for aspiring archaeologists, and showed that the area was especially rich in finds from the Roman period, with over 1500 objects found in the preceding year.
In July 2020, metal detectorist Luke Mahoney, found 1061 silver hammered coins estimated to be worth £100,000 in Ipswich. The coins dated back to the 15th-17th century, according to experts.
In September 2020, archaeologists announced the discovery of an Anglo-Saxon cemetery with 17 cremations and 191 burials dating back to the 7th century in Oulton, near Lowestoft. The graves contained the remains of men, women and children, as well as artefacts including small iron knives and silver pennies, wrist clasps, strings of amber and glass beads. According to Andrew Peachey, who carried out the excavations, the skeletons had mostly vanished because of the highly acidic soil. They, fortunately, were preserved as brittle shapes and “sand silhouettes” in the sand.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
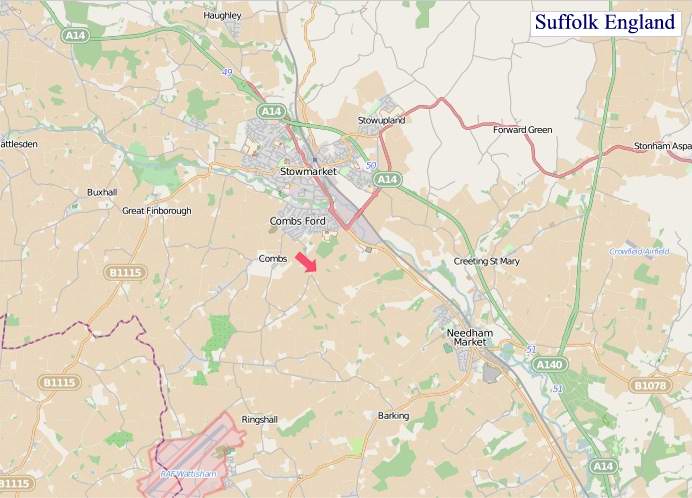
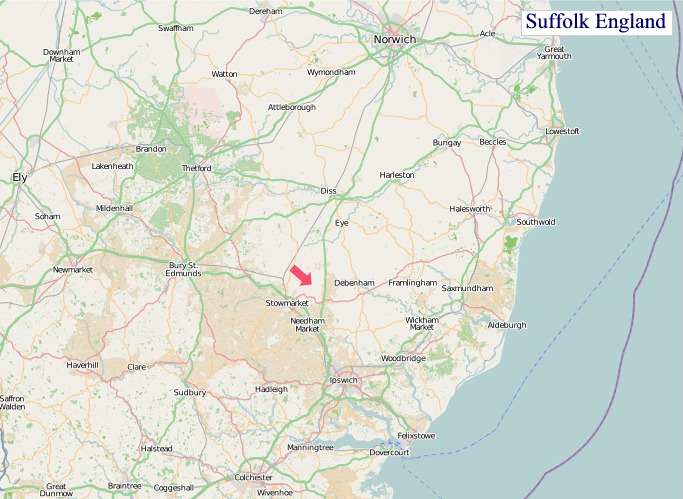
"© OpenStreetMap contributors, CC BY-SA".
Districts of Suffolk
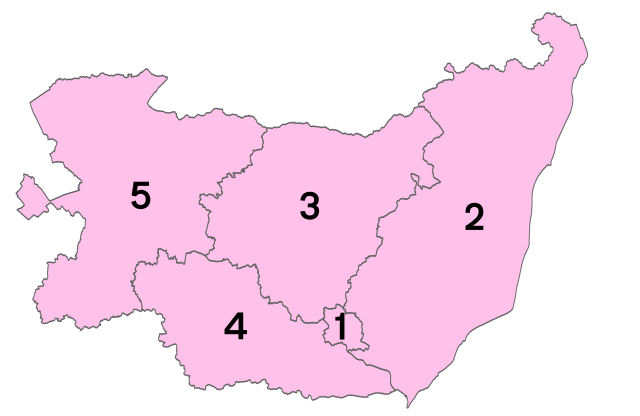
1 - Ipswich
2 - East Suffolk
3 - Mid Suffolk
4 - Babergh
5 - West Suffolk
Music



